Everything You Need to Know About Psoriasis
Click Here For Your Consultation
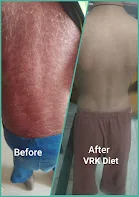
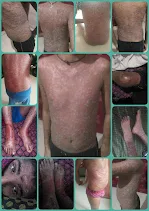
At Cell Health Clinic, we understand the challenges that come with managing Psoriasis, a complex autoimmune condition. Our expert team focuses on personalized treatment plans that combine Naturopathy and the VRK PMF Diet to help alleviate symptoms and improve your quality of life. By identifying triggers and incorporating nutrient-rich foods, such as those high in omega-3 fatty acids, we aim to reduce inflammation and support skin health. The VRK PMF Diet is designed to address metabolic imbalances and promote overall wellness. We offer holistic care that addresses not just the physical symptoms but also the emotional well-being of our patients, ensuring a comprehensive approach to healing. Let us help you reclaim your skin and confidence!
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells. This buildup leads to scaly, dry, or itchy skin. With certain lifestyle changes and medications, psoriasis can be managed effectively. Additionally, tracking and identifying possible triggers can help reduce flare-ups.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis causes inflammation and redness around scaly patches. These scales typically appear whitish-silver on light skin and more purplish, dark brown with gray scales on darker skin. In some cases, patches may crack and bleed.
- Common Symptoms:
- Raised, inflamed patches of skin
- Whitish-silver or gray scales
- Dry, cracked skin
- Soreness, itching, or burning sensations
- Thick, pitted nails
- Painful, swollen joints
What Causes Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is the result of a sped-up skin production process. In healthy individuals, skin cells have a life cycle of about 28 days. In psoriasis patients, this process can occur in just a few days, leading to skin cell buildup.
- Two Key Factors:
- Genetics: A family history of psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Immune System: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder, where white blood cells mistakenly attack healthy skin cells, causing rapid cell production and inflammation.
Types of Psoriasis
There are five main types of psoriasis:
Plaque Psoriasis:
- The most common type (80–90% of cases).
- Causes red, inflamed patches with whitish-silver scales on light skin and purple or brown patches on darker skin.
Guttate Psoriasis:
- Appears as small pink or violet spots, mainly on the torso, arms, and legs.
- Commonly affects children.
Pustular Psoriasis:
- Characterized by pus-filled blisters and inflamed skin.
- Typically localized to smaller areas like hands or feet but can be widespread.
Inverse Psoriasis:
- Appears as bright, red, shiny inflamed skin.
- Commonly found under the armpits, breasts, or around the groin and genitals.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis:
- A severe and rare form that can cover large sections of the body, causing skin to slough off in sheets.
- This type can be life-threatening, requiring immediate medical attention.
Psoriasis and Associated Conditions
Psoriasis is linked with several other health conditions, including:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Heart disease
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Anxiety and depression
Psoriasis Triggers
Psoriasis flare-ups are triggered by various factors, including:
- Stress: High stress levels can exacerbate the condition.
- Alcohol: Excessive drinking may increase flare-ups.
- Injury: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburn can trigger new outbreaks.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as lithium and high blood pressure medication, can trigger psoriasis.
- Infections: Infections like strep throat can also contribute to flare-ups.
Living with Psoriasis
Managing psoriasis involves lifestyle adjustments, including:
Diet:
- Focus on nutrient-dense foods like omega-3 fatty acids, whole grains, and plants.
- Limit foods that may increase inflammation, such as refined sugars and highly processed foods.
Stress Management:
- Consider meditation, journaling, yoga, and breathing exercises to reduce stress and prevent flare-ups.
Emotional Health:
- Living with psoriasis can impact self-esteem and lead to depression. It's important to seek support from family, friends, or a professional network.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Around 30–33% of people with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain, swelling, and inflammation. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent severe complications such as joint damage.
Psoriasis Statistics
Psoriasis affects approximately 7.5 million American adults. While it can begin at any age, most diagnoses occur between the ages of 15 and 35. People with psoriasis are also more likely to develop other conditions like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Summary
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition caused by an autoimmune response, leading to scaly lesions and potential joint complications. While it cannot be cured, the right lifestyle changes, treatments, and support systems can significantly improve quality of life.







Comments